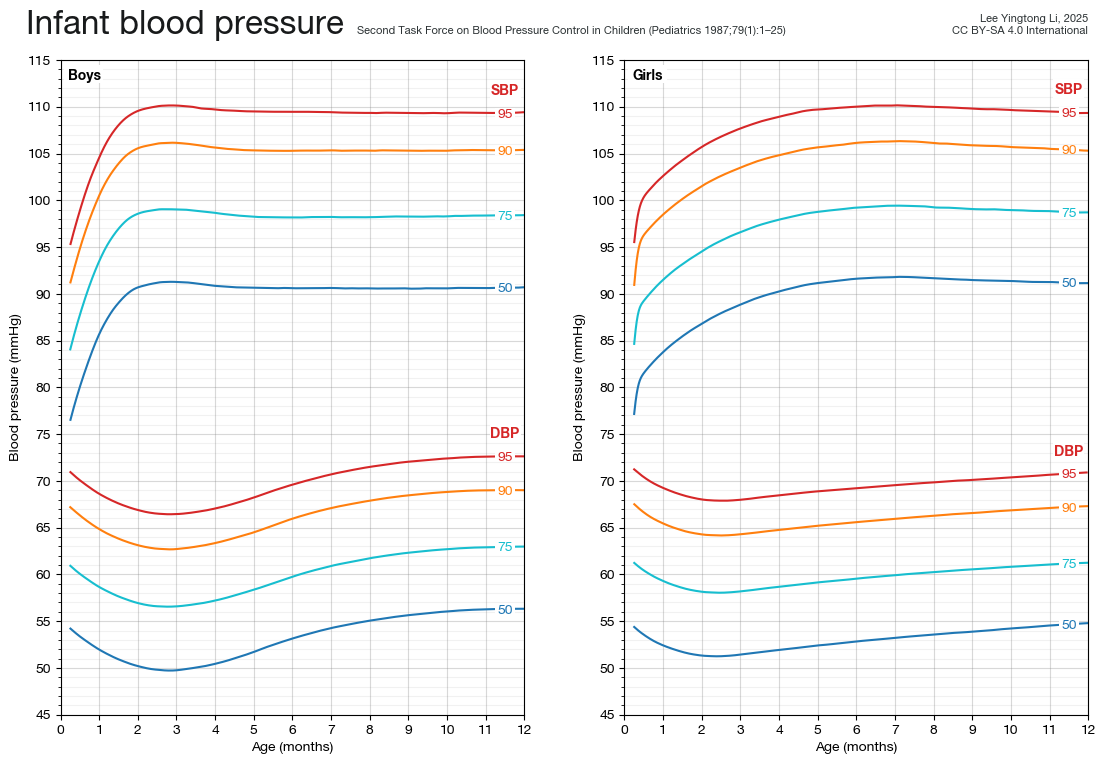
Infant blood pressure centiles from the Second Task Force on Blood Pressure Control in Children
Warning! The intended audience of this article is medical professionals and students. I am not your doctor. This article is not medical advice. This article has not been subject to formal peer review.
Below is presented a high-resolution centile chart for blood pressure in infants aged 7 days to 12 months, extracted from the report of the Second Task Force on Blood Pressure Control in Children.1
Methods
The Task Force report1 was obtained from the American Academy of Pediatrics (AAP) Publications website, where it is presented in scanned form with bitonal images embedded in PDF format. Figures 1 and 2 of the report were isolated from the PDF file in native resolution. To correct for rotation and scaling artifacts from scanning, a projective transformation was applied, using known coordinates read from the axis ticks or table of 90th centile values accompanying the figure. The coordinates chosen to define the projective transformation were the axis origin, tips of the x- and y-axes, and the 90th centile value at 12 months. Curve data was then extracted using standard image processing techniques, and compared to the report by visual inspection, and by comparison to the table of 90th centile values. If required, the projective transformation was adjusted to ensure that the extracted curve data accorded with the listed 90th centile values. The extracted curve data accords with the listed 90th centile values in all cases except for systolic blood pressure in girls at 0 months; extraction of curve data at this point was not possible using this methodology due to overlap between multiple curves at this point.
The curve data was then plotted to yield a high-resolution centile chart. Gaussian smoothing, with a standard deviation of 8 pixels, was used to reduce artifact arising from the bitonal scan. Data for ages less than 7 days was omitted from the chart, both due to the overlapping curves for systolic blood pressure in girls at 0 months, and because newer blood pressure norms are available for neonates.2
The code used to extract the curve data and generate the centile chart is available here.
Remarks
It is noted that, although the Task Force norms remain currently recommended by guidelines,2 they are based on Doppler ultrasound measurements and not oscillometric measurements, and differences have been detected in more recently published data.2 The limitations of the Task Force norms are discussed in detail in the guidelines by Dionne et al.2
References
- Task Force on Blood Pressure Control in Children. Report of the Second Task Force on Blood Pressure Control in Children: 1987. Pediatrics. 1987;79(1):1–25. doi: 10.1542/peds.79.1.1
- Dionne JM, Abitbol CL, Flynn JT. Hypertension in infancy: diagnosis, management and outcome. Pediatr Nephrol. 2012;27:17–32. doi: 10.1007/s00467-010-1755-z