-
Model rules for a computerised STV election using the weighted inclusive Gregory method
OpenTally is open-source software for counting single transferable vote (STV) elections. The default preset in OpenTally is ‘OpenTally WIGM’, a recommended set of simple STV rules designed for computer counting, using the weighted inclusive Gregory method, exact quotas and rational arithmetic.
The weighted inclusive Gregory… »
-
Compiling I D Hill's New Zealand Meek STV implementation: OpenTally dev log
In [1], I D Hill describes an implementation of Meek STV written in Pascal, which had been privately circulated since as early as 1999 [2]. The implementation is similar to the earlier ‘Algorithm 123’ Pascal implementation of Meek STV by Hill, Wichmann and… »
-
Multiple constraints in STV elections: OpenTally dev log
OpenTally is open source software currently under development for the counting of elections using STV and related systems. Part of its feature set is the implementation of constraints on elections: for example, where a certain minimum or maximum number of candidates must be elected from… »
-
Porting Python to Rust/WebAssembly: OpenTally dev log
Background and motivation
pyRCV2 is software for open-source election counting. It is intended to be usable across multiple platforms – as a web application, for the convenience of users less technologically inclined, and as a standalone CLI desktop application, for better performance. To this end,… »
-
pyRCV2: Open-source online counting for STV and other preferential voting systems
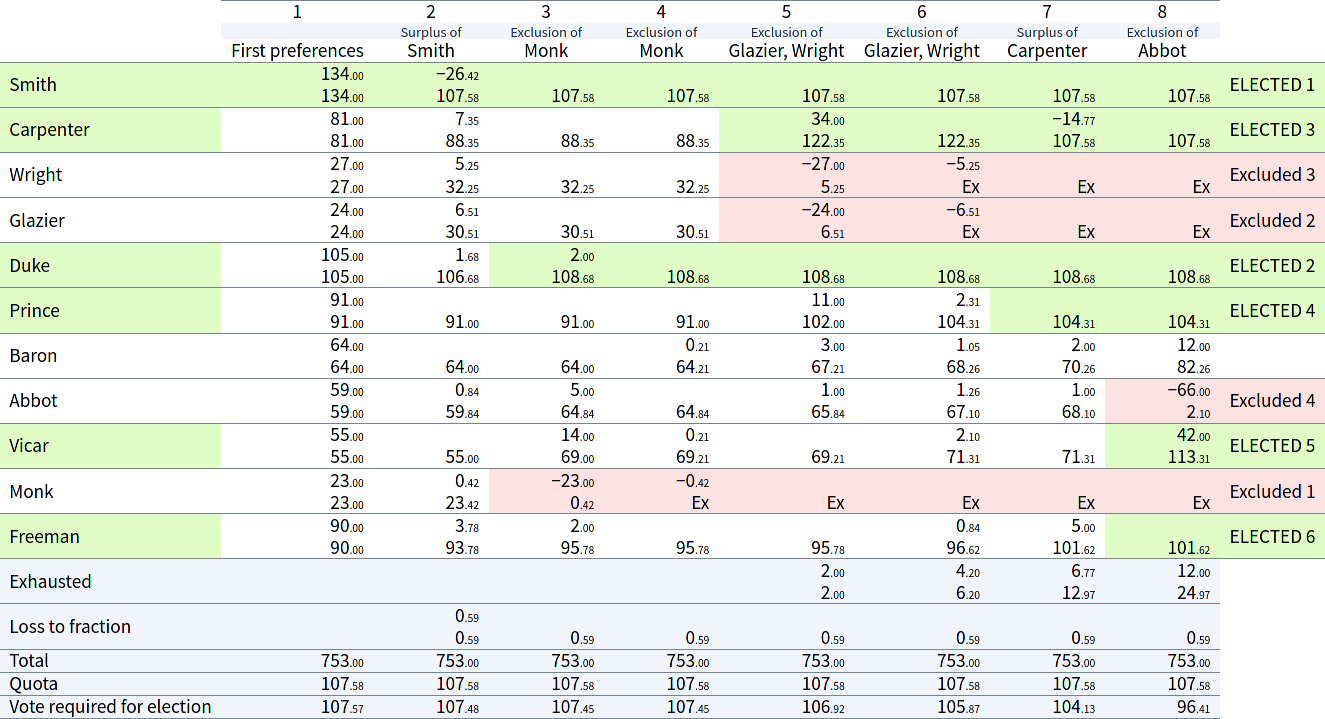
pyRCV2 is an application for counting various preferential voting elections.
pyRCV2 may be used in a number of different ways:
- as an online web application, no installation or special software required, at https://yingtongli.me/rcv/
- as a standalone Python command line application
- as a library within another
-
Single Transferable Vote counting sheets and worksheets (Creative Commons)
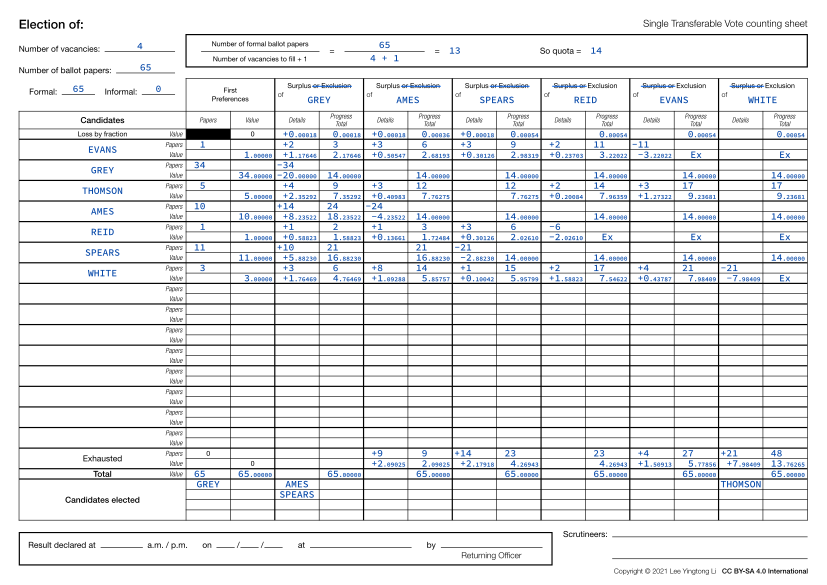
STV count sheet:


-
Why are the D'Hondt (quotient) and Jefferson (quota) methods equivalent?
The D'Hondt method/Jefferson method is a highest averages voting system (or apportionment method). While D'Hondt is usually described using successive division to calculate various quotients, Jefferson is usually described using a quota. It is known that the two systems produce the same results, but why?… »